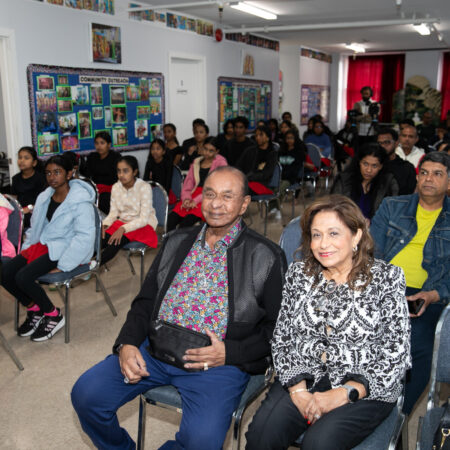
Diagnosis of dengue is considered when sudden high fever is accompanied by severe body, muscle or joint pain. It is important to be evaluated when a person develops fever within two weeks of being in the tropics or sub-tropics. Dengue often causes symptoms that are similar to other diseases such as flu, measles, and typhoid fever etc. Hence investigations are always performed to exclude other disease conditions. Usually, the blood of the patient is tested for the presence of antibodies and virus. Diagnosis of dengue infection can be done by the following methods:
Isolating the virus by collecting serum sample from patients within 5 days of appearance of symptoms.
Detection of specific antibodies can be done by collecting serum within 6 days after onset of symptoms. The serum is tested for specific anti-dengue antibodies by Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). Titres of IgM and IgG antibodies increase four-fold in serum sample.
Using Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) for detecting viral genomic sequence from Serum or Cerebro Spinal Fluid (CSF) samples collected from the patient, which is more expensive and complicated.
Courtesy of www.medindia.net

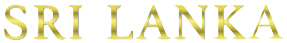






![TV-Poster-All-Exhibition-Sri-Lanka-in-Focus-USA-2025[1]](https://www.srilankafoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/TV-Poster-All-Exhibition-Sri-Lanka-in-Focus-USA-20251-450x450.jpg)